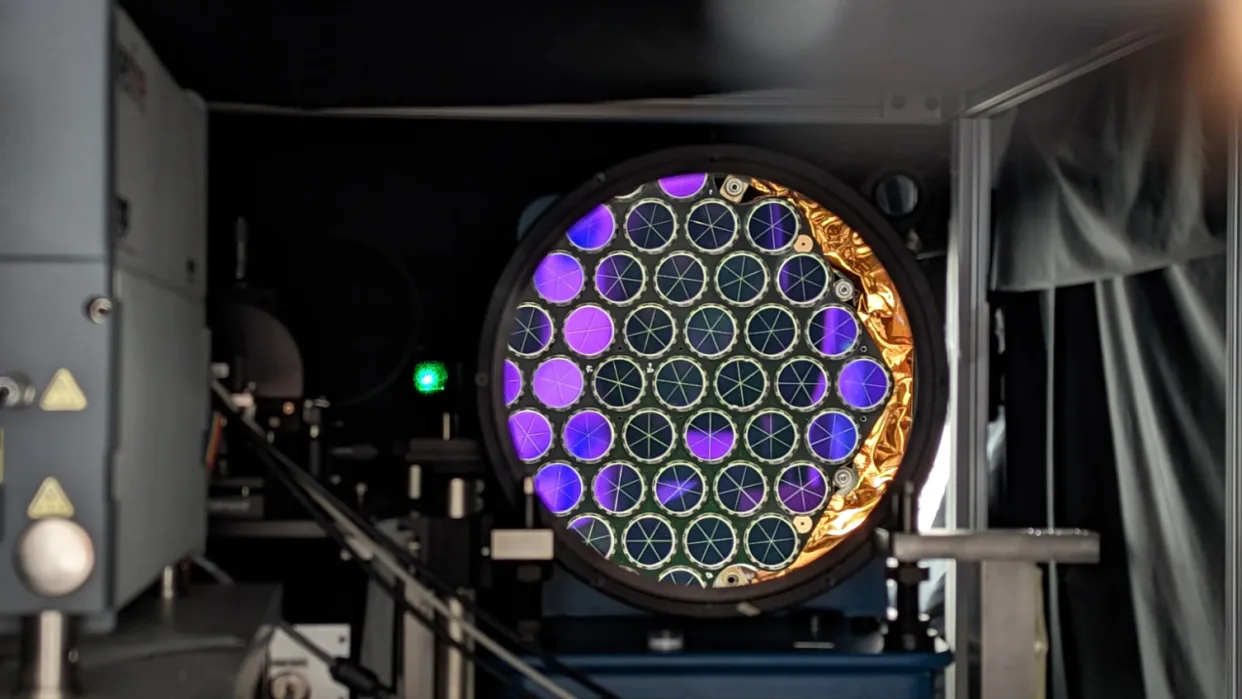
The US Space Force plans to launch two GPS satellites in 2025, called SV9 and SV10, that will carry laser retroreflector arrays (LRAs) to help determine the precise location of Earth’s center.
The LRAs will use a technique called Satellite Laser Ranging (SLR) where pulses of laser light are reflected between the satellites and ground stations. This allows precise distance measurements to within centimeters.
The data gathered by the LRAs will help researchers better monitor small changes in Earth’s center caused by events like earthquakes and tsunamis.
The LRAs were provided by NASA and the Naval Research Laboratory. They will be operated by the Space Force once integrated onto the GPS III satellites by Lockheed Martin.
Having more accurate positioning is crucial for applications like geodesy research into determining variations in Earth’s shape, rotation and gravitational field over time.
This collaboration between Space Force, NASA and NGA aims to advance space-based geodesy capabilities years ahead of schedule through upgrades to existing GPS satellites.
Source: Space