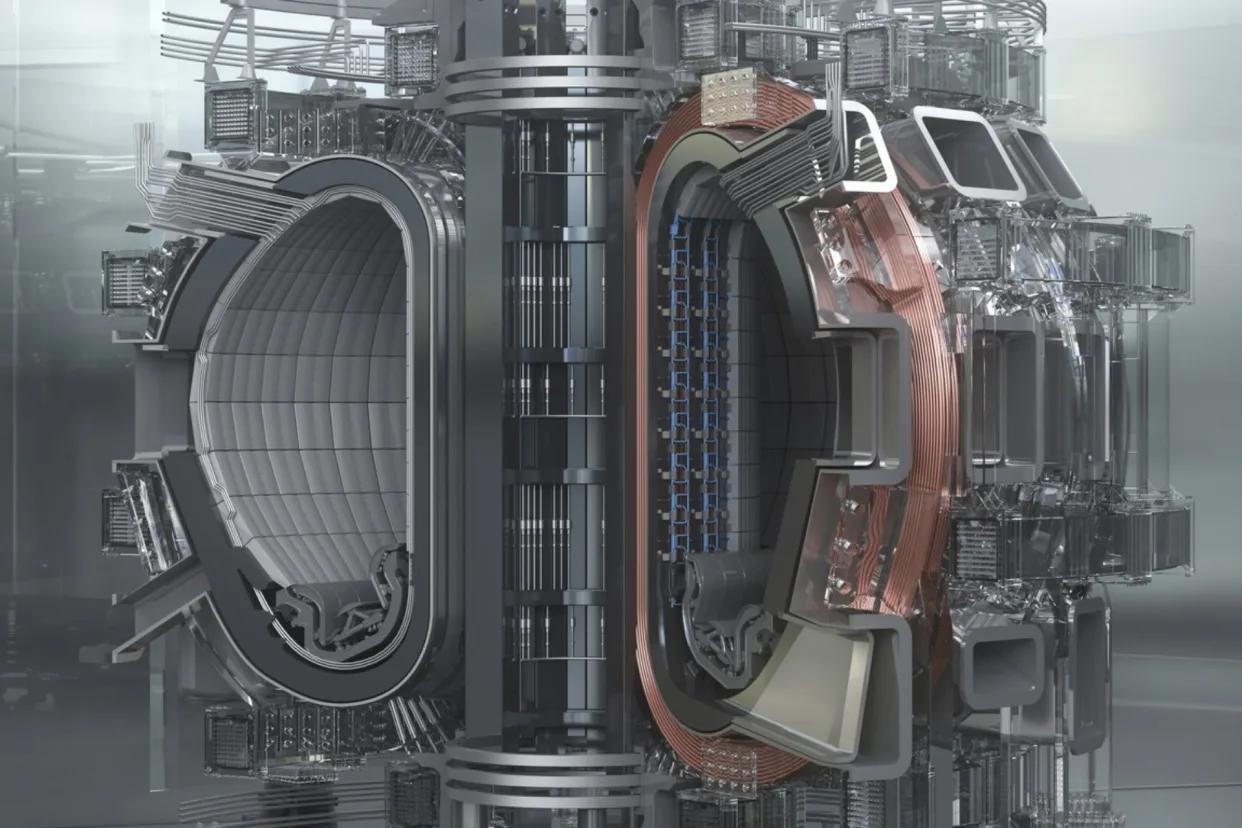
Scientists at the University of Wisconsin achieved a major milestone in nuclear fusion research by confining plasma at 17 Tesla using high-temperature superconducting magnets. This set a new world record for magnetic field strength used to contain fusion plasma.
The magnetic confinement experiment uses an upgraded “magnetic mirror” design which was a leading fusion concept in the 1980s but fell out of favor. The new design employs powerful rare-earth magnets to trap energetic plasma in a “magnetic bottle”.
Fusion processes involve fusing atomic nuclei to produce energy, unlike fission which splits atoms. If controlled fusion technology is achieved it could provide limitless clean energy by replicating the fusion processes that power the sun.
Experts say breakthroughs like this upgraded magnetic mirror experiment keep the promise of fusion energy on track to potentially serve as the “third pillar” of renewable energy along with solar and wind to enable full decarbonization. However, commercial fusion reactors are still estimated to be many years away.
Source: TCD