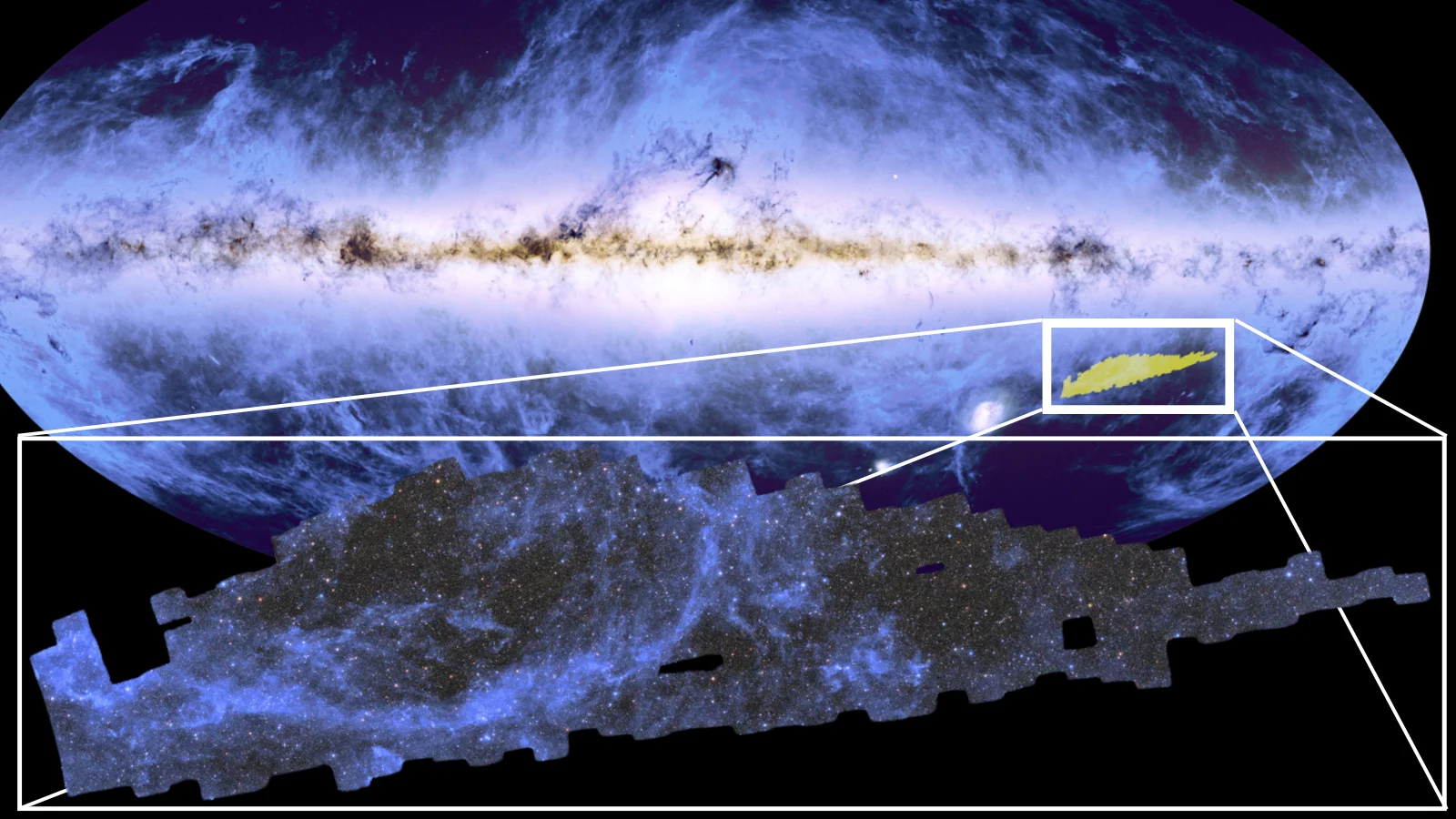
The Euclid Space Telescope has revealed the “first page” of the cosmic atlas it is building. The section of the map of the cosmos being built by Euclid was released on Monday (Oct. 15), and it features tens of millions of stars within the Milky Way and around 14 million distant galaxies beyond our own.
The vast cosmic mosaic was constructed from 260 Euclid observations collected between March 25 and April 8, 2024 and contains 208 gigapixels of data. The region charted is around 500 times as wide as the full moon appears in the sky over Earth.
Perhaps most astoundingly, the mosaic accounts for just 1% of the total survey Euclid will conduct over the next six years as it tracks the shapes, distances and movements of galaxies as far as 10 billion light-years away. Not only will this result in the largest 3D map of the cosmos ever created, but the vast scale of this map will help scientists investigate the mysteries of dark matter and dark energy, sometimes collectively known as the “dark universe.”

“This stunning image is the first piece of a map that in six years will reveal more than one-third of the sky,” Valeria Pettorino, Euclid Project Scientist at the European Space Agency (ESA), said in a statement. “This is just 1% of the map, and yet it is full of a variety of sources that will help scientists discover new ways to describe the universe.”

Cosmic atlas or “dark universe detective” casefile?
Launched in July 2023, Euclid began making scientific observations in February. This wide-angle space telescope with a 600-megapixel camera is able to record visible light and near-infrared light using a spectrometer. This enables us to measure “redshift,” the changes in which wavelengths of light reach us caused as galaxies race away from the Milky Way.
By doing this for a wide array of galaxies, Euclid can measure the effect of dark energy, the mysterious force driving the acceleration of the universe, by expanding the space between galaxies.
“Euclid is observing the universe in a brand new way, and it’s gonna get a gigantic census of the galaxies,” Universidad ECCI cosmologist Luz Ángela García Peñaloza told Space.com. “Any image that reveals information about the distribution of galaxies in the large-scale structure of the universe will provide handfuls of information on the nature of the dark side of the cosmos.
“We still need to wait a bit more to recover a larger sample of galaxies to infer cosmological parameters and rule out some existing models.”

Despite representing just two weeks of observations, the Euclid spacecraft’s sensitive cameras captured a wide array of objects in great detail for this new release.
One feature that will captivate scientists in this Euclid mosaic is the dim clouds that can be seen stretching between stars within the Milky Way. These appear in the wider images as light blue streaks against the black background of space.

These blue tracks are a mix of gas and dust and are sometimes referred to as “galactic cirrus” because they look like cirrus clouds in the skies over Earth. Euclid’s ability to visualize these clouds comes from the fact that they reflect optical light from the Milky Way and shine brightly in far-infrared light.

Taking a wider view of the cosmos and then narrowing down, the deep detail facilitated by Euclid allows astronomers to zoom very deep into the mosaic and see intricate structures, such as the shape of the spiral galaxy ESO 364-G036, which is located around 420 million light-years away.
This first page of the Euclid cosmic atlas and a tiny slice of the map of the universe that it will eventually create is simply a teaser for greater things to come from the mission.
Related Stories:
— Euclid ‘dark universe’ telescope is back on track after finding its guiding stars
— Euclid ‘dark universe’ telescope captures 1st full-color views of the cosmos (images)
— How will Europe’s Euclid space telescope see into the dark universe?
Around 12% of Euclid’s planned data collection has been completed, and the release of 53 square degrees of the survey, including a preview of the Euclid Deep Field areas, is planned for March 2025. The mission’s first year of cosmology data will be released to the scientific community in 2026.
“This is just the beginning of what we will be able to see in Euclid’s lifetime,” García Peñaloza concluded. “For sure, the best is still to come! I’m positive Euclid will shed light on our understanding of the cosmic mysteries.”
ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher and the space agency’s Director of Science Carole Mundell revealed the Euclid mosaic at the International Astronautical Congress in Milan, Italy.