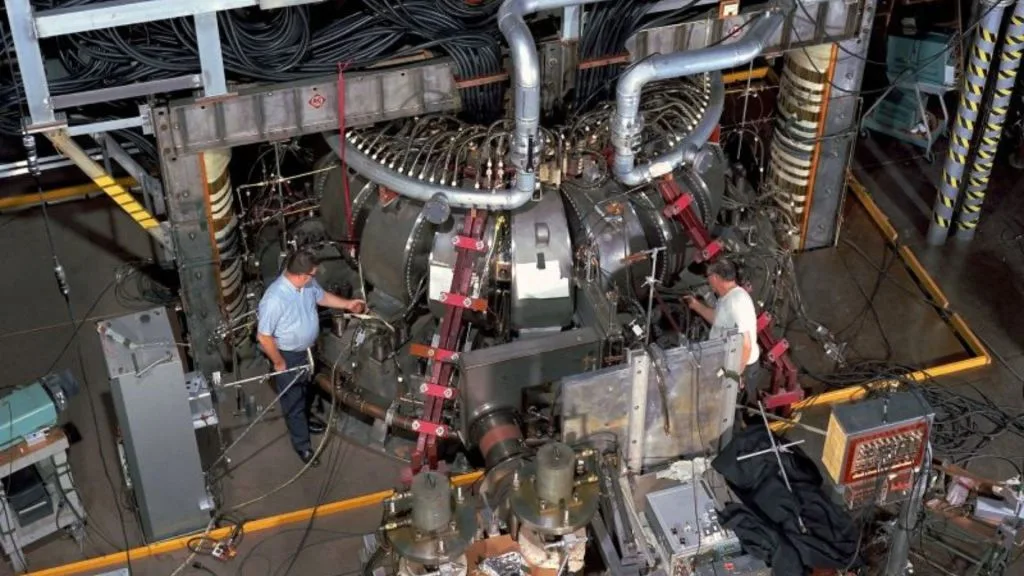
Scientists at the US Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory have made a significant breakthrough in improving the efficiency of nuclear fusion reactors.
They found that by adjusting the ratio of deuterium and tritium in the fuel mix, and using a process called spin polarization to align the quantum spins of the fuel atoms, the efficiency of the tritium burn in fusion reactions can be substantially improved.
This approach could lead to a 10-fold reduction in the amount of tritium required for fusion reactions. Tritium is a rare and radioactive isotope that has been a major hurdle for fusion energy development.
Reducing the tritium requirement has several practical benefits, including lowering the risks and costs associated with handling and storing radioactive materials, as well as allowing for smaller and more efficient fusion power plant designs.
This is the first time researchers have explored how spin-polarized fuel could boost tritium-burn efficiency, representing an important step forward in making fusion power a viable clean energy solution.
Source: interestingengineering